Left unchecked, technical debt will ensure that the only work that gets done is unplanned work! -Gene Kim, The Phoenix Project
Technical debt is a measure of the amount of duct tape holding your system together, plus the amount of rust that it has accumulated. -Itzy Sabo
Identifying and managing healthcare IT investments is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and providing the highest standard of patient care. This article breaks down the idea of technical debt, lays out some related risks, and prioritizes healthcare IT investments to help groups avoid technical debt and its associated risks. By the end, you’ll better understand the concept of technical debt, why it matters, and how to start paying it down.
What is Technical Debt?
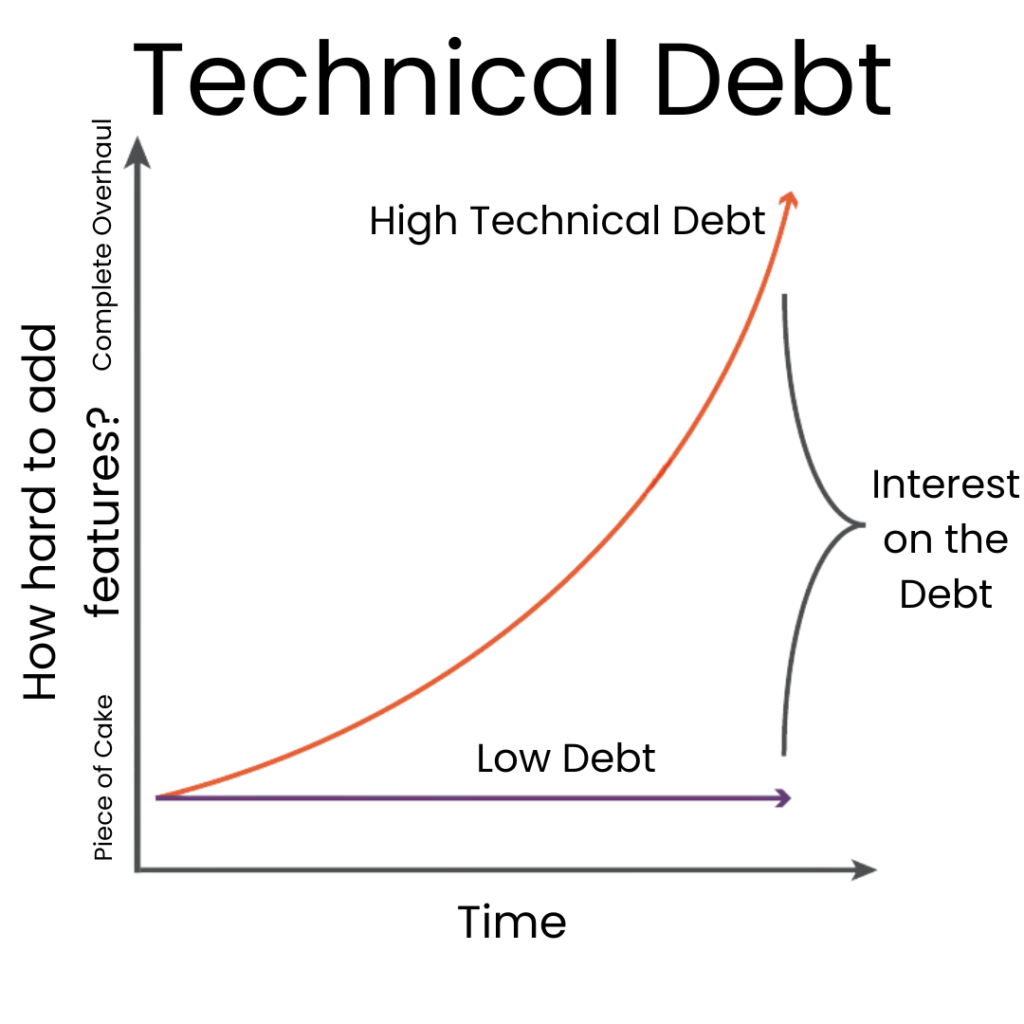
Technical debt arises when healthcare organizations delay essential technology investments, hoping to save on costs in the short term. It is “technical” in that it relates to technology decisions made about your business, such as which email system to use, which software your company runs on, where that software lives, and how much of what your company does is in the cloud.
It is “debt” in financial terms because it relates to a deficit from bad decisions. The debt deepens when a best practice recommendation is avoided for some time, exposing your company to risk. This risk can be in the form of cybersecurity hacks. It can also manifest as lost productivity due to extra steps in workflows or time spent logging into older systems. Decisions made (or not made) have repercussions for as long as you’re in business. The difference between best practice and the decision made is Technical Debt.
Example Risks from Rising Technical Debt
The risk created by allowing technical debt to grow affects many different areas of your business.
- Legacy Infrastructure: Using outdated hardware or infrastructure can result in slow performance, frequent downtime, and difficulty scaling up to meet growing demands.
- Insufficient Security Measures: Inadequate cybersecurity measures could leave the practice vulnerable to data breaches, compromising patient confidentiality and leading to legal and financial repercussions.
- Manual Processes: Relying on manual processes for tasks such as appointment scheduling, patient registration, or billing can be time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inefficiencies and potential revenue loss.
- Lack of Integration: If various systems within the practice (e.g., scheduling, billing, EHR) are not properly integrated, it can lead to duplicate data entry, discrepancies between systems, and increased risk of errors.
- Outdated Electronic Health Record (EHR) System: If the practice uses an outdated or poorly designed EHR system, it could lead to inefficiencies in patient care, documentation errors, and staff frustration.
Main Focuses for Healthcare IT Investment Spend
To mitigate technical debt, healthcare facilities should proactively prioritize their tech investments in three key areas:
- Operational Technology: Includes the systems necessary for day-to-day healthcare operations. These should be fully funded to avoid deferred costs that accrue as technical debt and can cause operational inefficiencies, including downtime.
- Business Enhancement Technology: This area focuses on technology that can improve healthcare delivery, patient experience, and administrative efficiency, keeping your facility competitive.
- Innovative Technology: This term pertains to investments in transformative technology that can open new revenue streams or fundamentally change service delivery.
A balanced allocation for a healthcare technology budget could be 75% for operations, 15% for enhancement, and 10% for innovation. This strategy ensures sustainability and positions healthcare organizations to take advantage of new opportunities without compromising current operations or incurring debt.
| Example Current Technical Debt | $ 295,320 | ||||
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| HealthSafeIT | $ 265,440 | $ 265,440 | $ 265,440 | $ 265,440 | $ 1,061,760 |
| Technical Debt | $ 295,320 | $ 180,000 | $ 64,680 | $ – | $ – |
| Total IT Liability | $ 560,760 | $ 445,440 | $ 330,120 | $ 265,440 | $ 1,061,760 |
| Traditional IT | $ 156,000 | $ 163,800 | $ 171,990 | $ 180,590 | $ 672,380 |
| Technical Debt | $ 295,320 | $ 354,384 | $ 425,261 | $ 510,313 | $ 510,313 |
| Lost Productivity | $ 300,000 | $ 300,000 | $ 300,000 | $ 300,000 | $ 1,200,000 |
| Total IT Liability | $ 751,320 | $ 818,184 | $ 897,251 | $ 990,902 | $ 2,382,692 |
In practice, this might look like the model provided above, which compares a proactive investment strategy in HealthSafeIT with a more traditional approach, revealing long-term cost savings and avoiding productivity losses associated with technical debt. The example shows a large practice with 160 employees that has accumulated almost $300,000 in technical debt. The traditional approach manages the technology, fixing things as they break and keeping things running.
With this approach, technical debt continues to grow at a rate of 20% a year, and the practice sees loss of productivity due to downtime, inefficient workflows, and poor technological performance. HealthSafeIT shows a consistent, budgeted amount each year that eliminates technical debt by year 3. This has been proven over time and is a real-life example of how HealthSafeIT maximizes an organization’s tech investments, creating a clear roadmap and making technology a driver, not a cost center.
Relevant Findings and Takeaways
Analyzing the sample data, HealthSafeIT’s model sustains a constant healthcare IT investment over four years, stabilizing technical debt and maintaining total IT liability at $1,061,760. In stark contrast, Traditional IT accumulates increasing technical debt and experiences lost productivity, leading to a total IT liability of $2,382,692 by year four. This represents a more than twofold increase compared to HealthSafeIT’s model, highlighting the financial impact of strategic healthcare IT investment and the avoidance of technical debt.
By investing wisely in technology today, healthcare organizations can avoid the compounding effects of technical debt and ensure that patients and providers benefit from a responsive, efficient, and forward-looking healthcare IT investment.


